High body temperature increases gut microbiota-dependent host resistance to influenza A virus and SARS-CoV-2 infection
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 02 May 2024
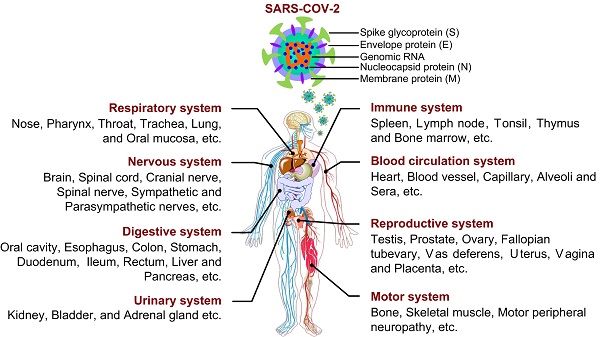
COVID-19: systemic pathology and its implications for therapy

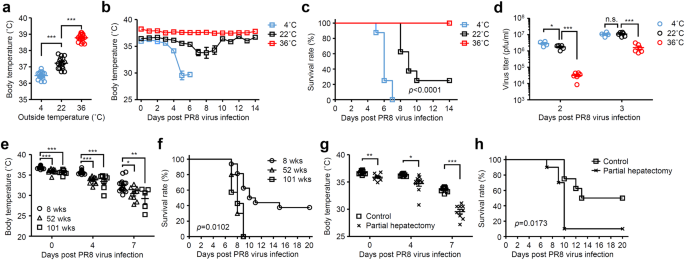
Core body temperature increases host resistance to influenza virus

High body temperature increases gut microbiota-dependent host resistance to influenza A virus and SARS-CoV-2 infection
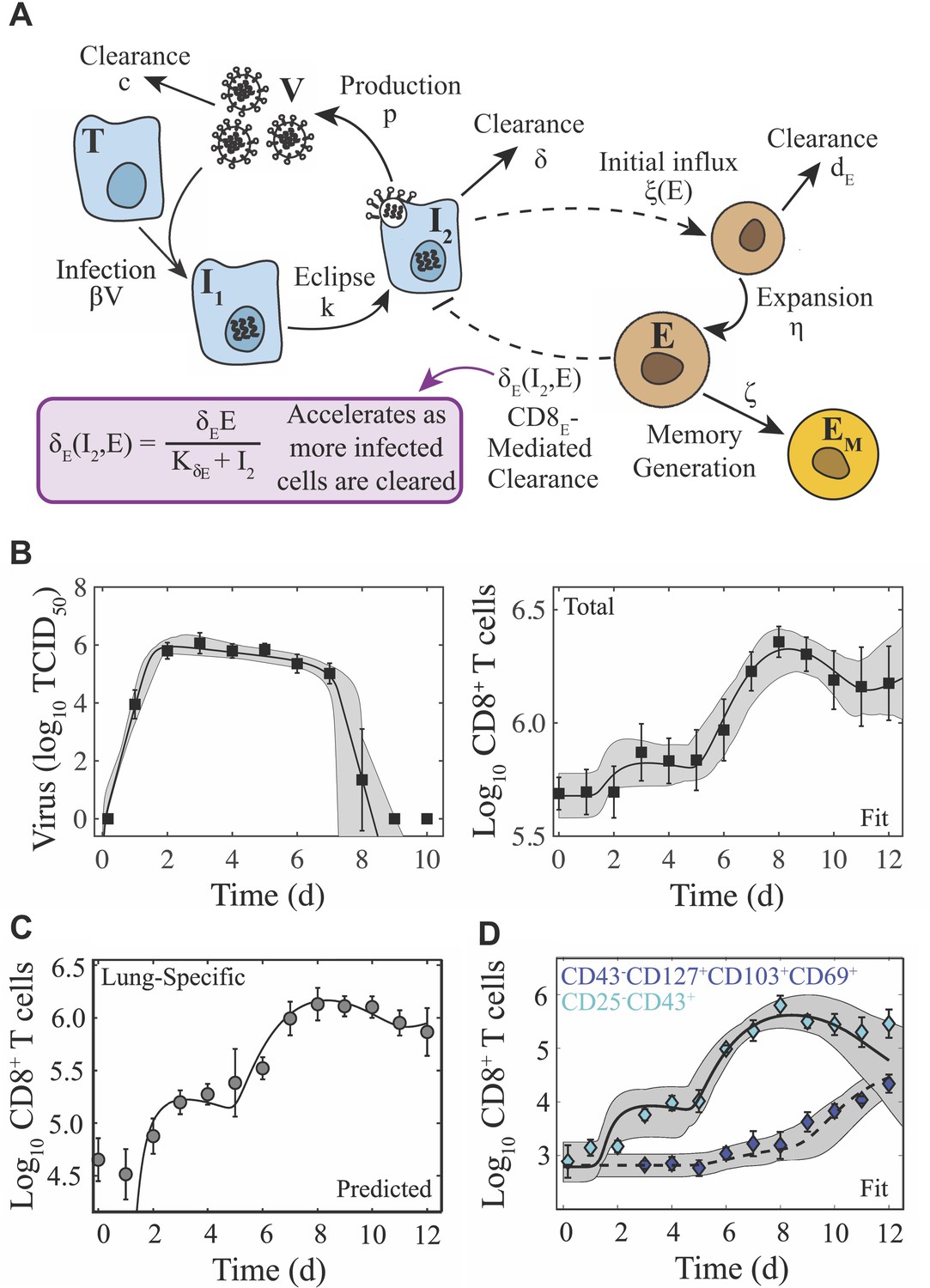
Dynamically linking influenza virus infection kinetics, lung injury, inflammation, and disease severity

東京大学医科学研究所 感染症国際研究センター ウイルス学分野
Dual and mutual interaction between microbiota and viral infections: a possible treat for COVID-19, Microbial Cell Factories
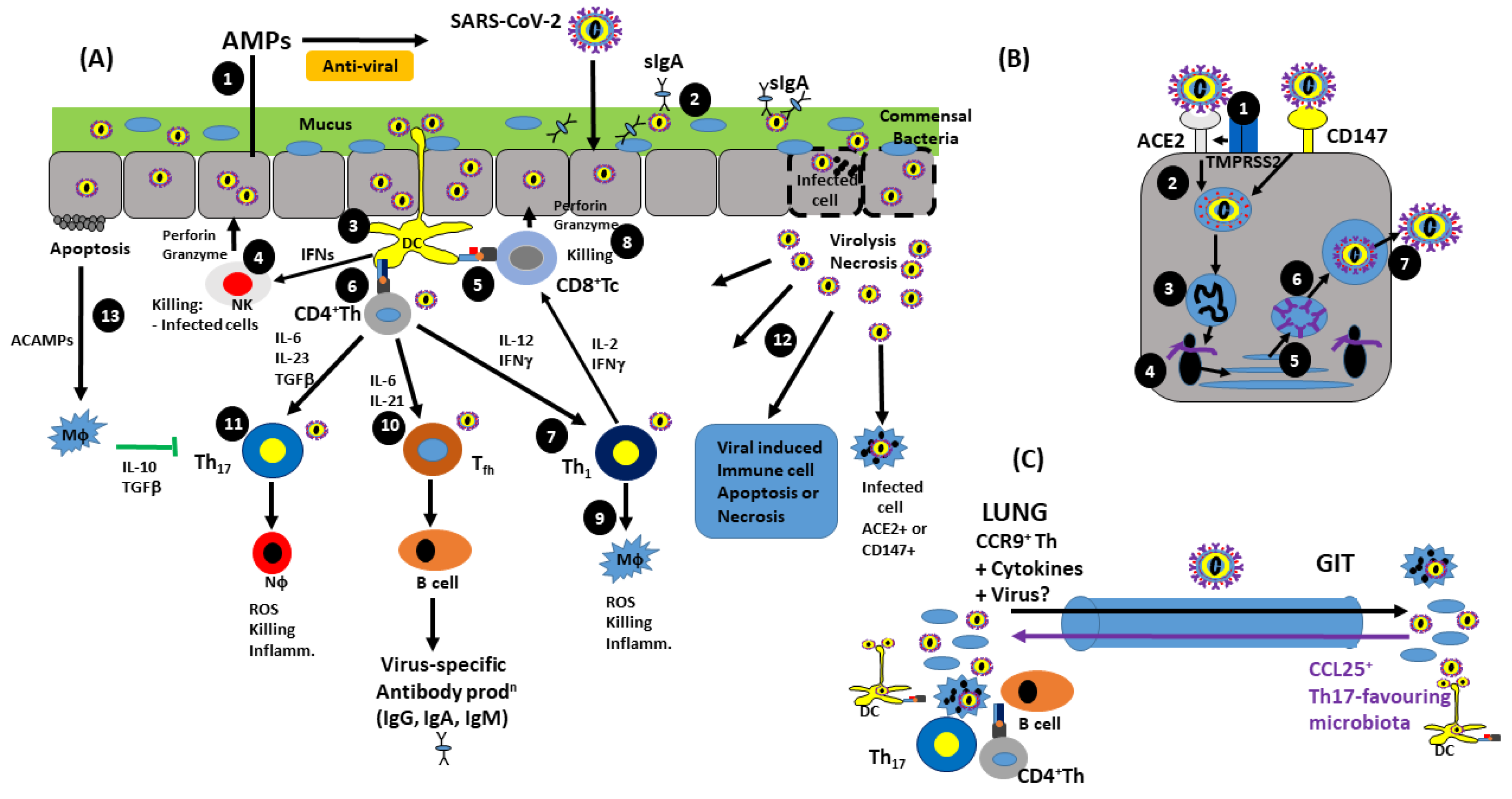
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

The central role of the nasal microenvironment in the transmission, modulation, and clinical progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection - Mucosal Immunology
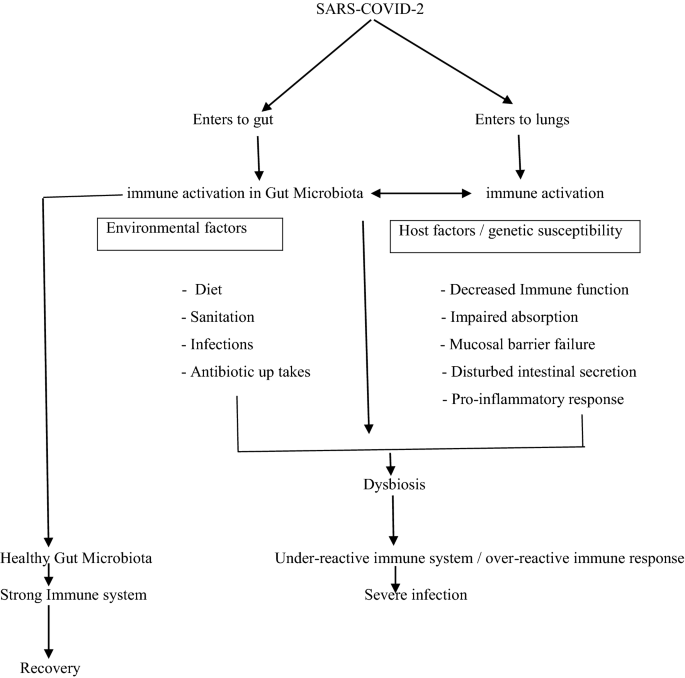
COVID-19 and Gut Microbiota: A Potential Connection

Mild SARS-CoV-2 infection results in long-lasting microbiota instability
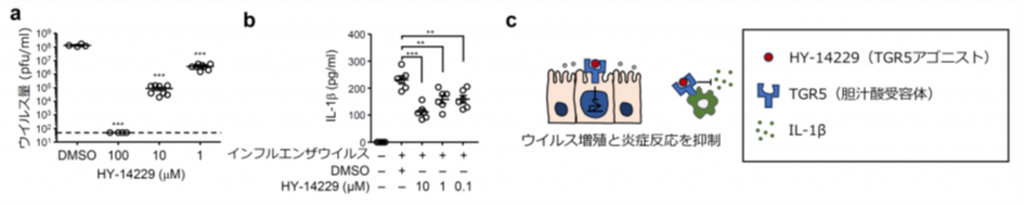
プレスリリース】発熱がウイルス性肺炎の重症化を抑制するメカニズムを
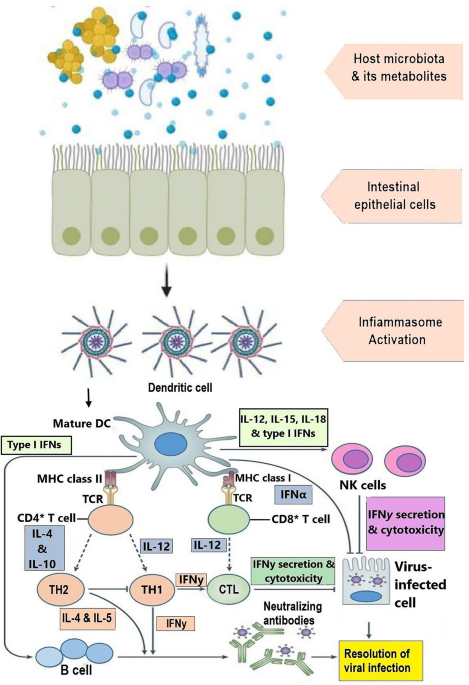
COVID-19 and Gut Microbiota: A Potential Connection
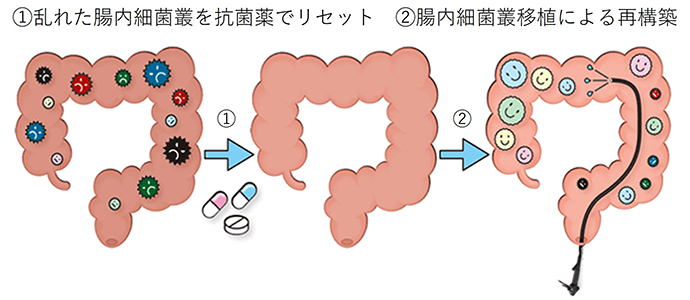
Gastroenterology Intestinal microbiota transplantation for
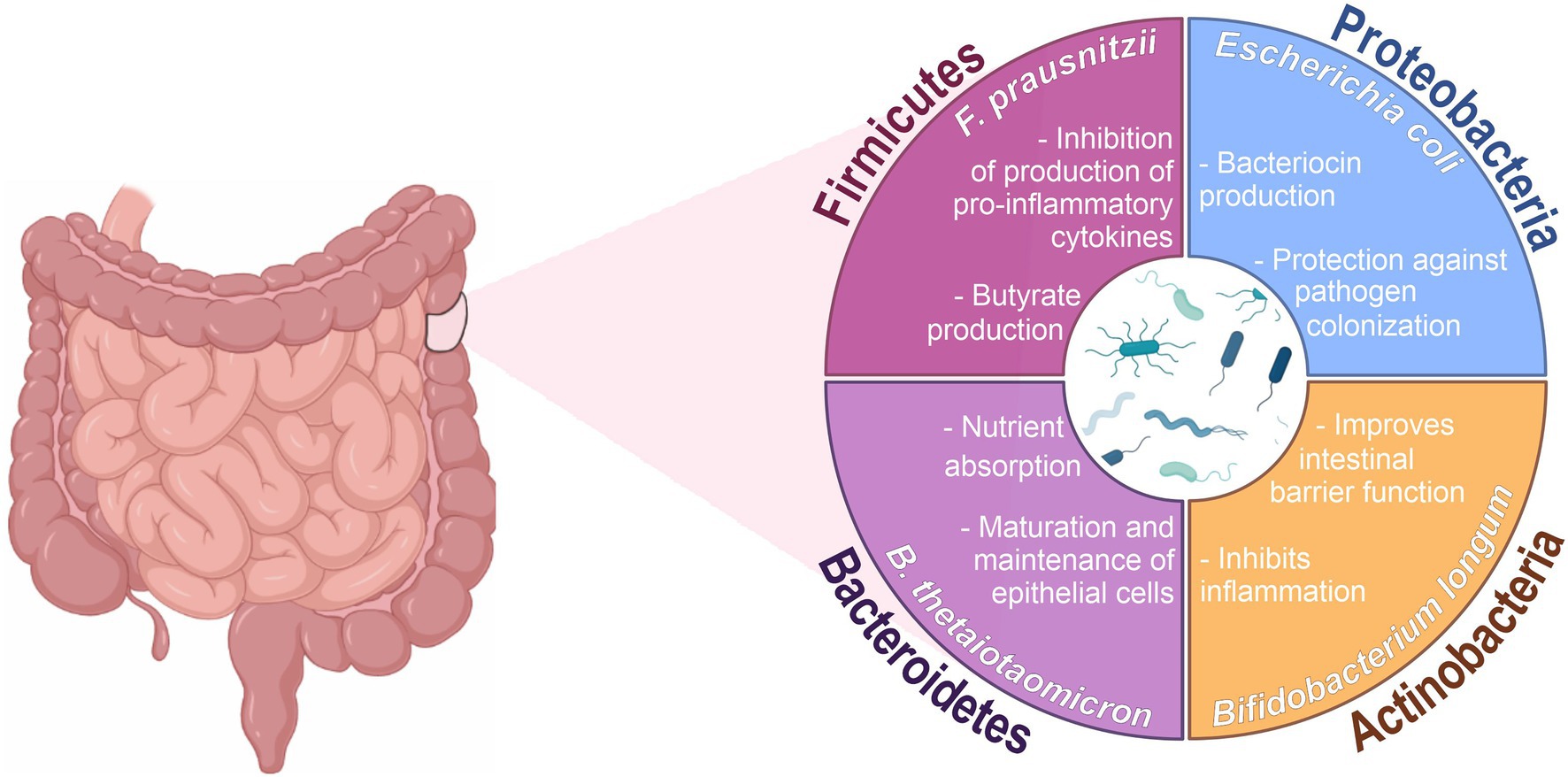
Frontiers Role of gut microbiota in infectious and inflammatory diseases

From the Role of Microbiota in Gut-Lung Axis to SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis
Recommended for you
 Roseola - NHS14 Jul 2023
Roseola - NHS14 Jul 2023 ASOS expands Face + Body range as viral trends and products drive demand14 Jul 2023
ASOS expands Face + Body range as viral trends and products drive demand14 Jul 2023 Ariana Grande's viral video reminds us why body comments can be especially harmful - CBS News14 Jul 2023
Ariana Grande's viral video reminds us why body comments can be especially harmful - CBS News14 Jul 2023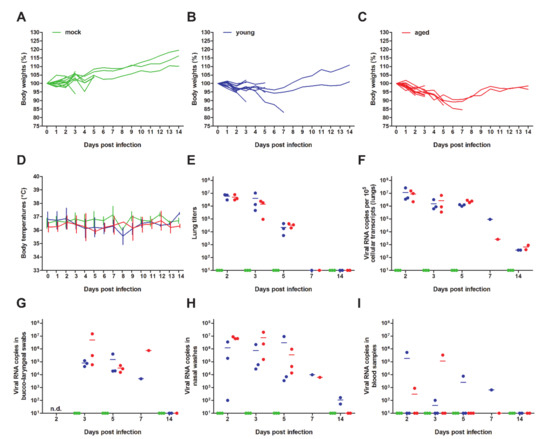 Viruses, Free Full-Text14 Jul 2023
Viruses, Free Full-Text14 Jul 2023 Wisconsin woman's old rant over Bath & Body Works goes viral on TikTok14 Jul 2023
Wisconsin woman's old rant over Bath & Body Works goes viral on TikTok14 Jul 2023 Social media, the 'bikini bridge' and the viral contagion of body ideals14 Jul 2023
Social media, the 'bikini bridge' and the viral contagion of body ideals14 Jul 2023 Prime Big Deal Days 2023: Sol de Janeiro Bum Bum Cream Sale14 Jul 2023
Prime Big Deal Days 2023: Sol de Janeiro Bum Bum Cream Sale14 Jul 2023 Viral vectors teach your body how to fight off COVID-19 : Oregon14 Jul 2023
Viral vectors teach your body how to fight off COVID-19 : Oregon14 Jul 2023 Basophilic viral inclusion body in the nucleus of a hepatocyte of14 Jul 2023
Basophilic viral inclusion body in the nucleus of a hepatocyte of14 Jul 2023 Arthritis-causing virus hides in body for months after infection14 Jul 2023
Arthritis-causing virus hides in body for months after infection14 Jul 2023
You may also like
 Black oh polly dress14 Jul 2023
Black oh polly dress14 Jul 2023 SUJETADOR AD SIRENA14 Jul 2023
SUJETADOR AD SIRENA14 Jul 2023- Why I Self-Pleasure — The Empowered Woman14 Jul 2023
- Women's Double-scoop Bodysuit - A New Day™ Taupe 4x : Target14 Jul 2023
 Buy Nykd by Nykaa Anti-Gravity Non WiBlack Non Padded Bra - Black14 Jul 2023
Buy Nykd by Nykaa Anti-Gravity Non WiBlack Non Padded Bra - Black14 Jul 2023 Macy's Black Friday in July sale is ON: The 18 best deals to shop now14 Jul 2023
Macy's Black Friday in July sale is ON: The 18 best deals to shop now14 Jul 2023- DOWNLOAD} Journey - Revelation {ALBUM MP3 ZIP} - Wakelet14 Jul 2023
- Braided Lines Tali Pancing Benang HERCULES 500M1500M2000M 414 Jul 2023
 Simpsons Swag14 Jul 2023
Simpsons Swag14 Jul 2023 Fashion items you'll need to put together just about any look14 Jul 2023
Fashion items you'll need to put together just about any look14 Jul 2023



